ຢູໂກສະລາເວຍ
ຢູໂກສະລາເວຍ (/ˌjuːɡoʊˈslɑːviə/; ແປວ່າ ທີ່ດິນຂອງ Slavs ພາກໃຕ້ ; Serbo-Croatian [ juɡǒslaːʋija ]; Slovene [ juɡɔˈslàːʋija ]; Macedonian [ juɡɔˈsɫavija ] [lower-alpha 1]) ແມ່ນປະເທດໃນ ພາກຕາເວັນອອກສ່ຽງໃຕ້ ແລະ ພາກກາງຂອງເອີຣົບ ທີ່ມີມາຈາກ 1918 ຫາ 1992. ມັນ ໄດ້ເກີດຂຶ້ນ ຫຼັງຈາກ ສົງຄາມໂລກຄັ້ງທີ 1, [lower-alpha 2] ພາຍໃຕ້ຊື່ຂອງ ອານາຈັກເຊີບ, Croats ແລະ Slovenes ຈາກການລວມຕົວຂອງ ອານາຈັກ Serbia ກັບ ລັດຊົ່ວຄາວຂອງ Slovenes, Croats ແລະ Serbs, ແລະປະກອບເປັນຄັ້ງທໍາອິດ. ສະຫະພັນຂອງຊາວ Slavic ໃຕ້ເປັນ ລັດອະທິປະໄຕ, ປະຕິບັດຕາມສັດຕະວັດຂອງການປົກຄອງຕ່າງປະເທດໃນພາກພື້ນພາຍໃຕ້ ຈັກກະວັດໂອສະມັນ ແລະ ລັດທິ Habsburg . ປີເຕີທີ I ຂອງເຊີເບຍ ເປັນ ອະທິປະໄຕຄັ້ງທໍາອິດ ຂອງຕົນ. ອານາຈັກໄດ້ຮັບການຍອມຮັບຈາກສາກົນໃນວັນທີ 13 ກໍລະກົດ 1922 ທີ່ ກອງປະຊຸມເອກອັກຄະລັດຖະທູດ ຢູ່ ປາຣີ . [7] ຊື່ທາງການຂອງລັດໄດ້ຖືກປ່ຽນເປັນ ຊະອານາຈັກ Yugoslavia ໃນວັນທີ 3 ຕຸລາ 1929.
ຢູໂກສະລາເວຍ Jugoslavija Југославија | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1918–1992 1941–1945: Axis occupation | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
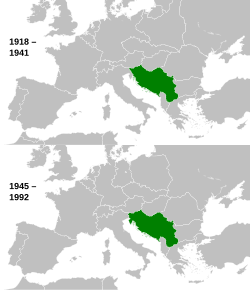 ຢູໂກສະລາເວຍ ໃນລະຫວ່າງ ໄລຍະສົງຄາມ (ເທິງ) ແລະ ສົງຄາມເຢັນ (ລຸ່ມ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ເມືອງຫຼວງ | Belgrade 44°49′N 20°27′E / 44.817°N 20.450°E | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ເມືອງໃຫຍ່ທີ່ສຸດ | ນະຄອນຫຼວງ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ພາສາລັດຖະການ | Serbo-Croato-Slovene (before 1944)
Serbo-Croatian (de facto; from 1944) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ເດມະນິມ | Yugoslav | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ການປົກຄອງ | ລະບອບຣາຊາທິປະໄຕເຊື້ອສາຍ (1918–1941) Federal Republic (1945–1992) ແມ່ແບບ:ລາຍຊື່ຫຍໍ້ໄດ້ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ປະຫວັດສາດ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
• Creation | 1 December 1918 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ວັນທີ 6 ເມສາ 1941 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ວັນທີ 24 ຕຸລາ 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ວັນທີ 29 ພະຈິກ 1945 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 27 ເມສາ 1992 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ປະຊາກອນ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1955 | 17,522,438[1] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1965 | 19,489,605[2] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1975 | 21,441,297[3] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1985 | 23,121,383[4] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
• 1991 | 23,532,279[5] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ສະກຸນເງິນ | Yugoslav dinar | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ລະຫັດໂທລະສັບ | 38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ລະຫັດອິນເຕີເນັດ | .yu | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||
ອ້າງອິງ
ດັດແກ້- ↑ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1955" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ↑ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1965" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ↑ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1975" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ↑ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1985" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ↑ "Statistical yearbook of Yugoslavia, 1991" (PDF). publikacije.stat.gov.rs. Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia Federal Statistical Office.
- ↑ Spencer Tucker. Encyclopedia of World War I: A Political, Social, and Military History. Santa Barbara, California, US: ABC-CLIO, 2005. Pp. 1189.
- ↑ "orderofdanilo.org".
{{cite web}}:|archive-url=requires|archive-date=(help);|archive-url=requires|url=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help)
- ↑ ອານບານີ: Jugosllavia; ແມ່ແບບ:Lang-rup; ແມ່ແບບ:Lang-hu; ແມ່ແບບ:Lang-rue; ແມ່ແບບ:Lang-sk; ຣູມານີ: Iugoslavia; ເຊັກ: Jugoslávie; ອິຕາລີ: Iugoslavia; ຕວັກກີ: Yugoslavya; ບູນກາລີ: Югославия
- ↑ The Yugoslav Committee, led by Dalmatian Croat politician Ante Trumbić, lobbied the Allies to support the creation of an independent South Slavic state and delivered the proposal in the Corfu Declaration on 20 July 1917.[6]



