ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງ
ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງ, ແມ່ນ ສະພາບທາງການແພດ ໄລຍະຍາວ ທີ່ ຄວາມດັນເລືອດ ໃນ ເສັ້ນເລືອດແດງ ສູງຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງ.[1] ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງມັກຈະບໍ່ເຮັດໃຫ້ເກີດອາການຂອງມັນເອງ.[2] ຢ່າງໃດກໍຕາມ, ມັນເປັນປັດໃຈສ່ຽງທີ່ສໍາຄັນສໍາລັບ ເສັ້ນເລືອດຕັນໃນ, ພະຍາດເສັ້ນເລືອດຫົວໃຈ, ຄວາມລົ້ມເຫຼວຂອງຫົວໃຈ, ໂຣກ atrial fibrillation, ພະຍາດເສັ້ນເລືອດແດງ peripheral, ການສູນເສຍສາຍຕາ, ພະຍາດຫມາກໄຂ່ຫຼັງຊໍາເຮື້ອ, ແລະ dementia.[3][4][5][6] ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງເປັນສາເຫດຕົ້ນຕໍຂອງການເສຍຊີວິດກ່ອນໄວອັນຄວນໃນທົ່ວໂລກ.[7]
ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງຖືກຈັດປະເພດເປັນ ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງ ຕົ້ນຕໍ (ທີ່ຈໍາເປັນ) ຫຼື ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງ ທີສອງ.[8] ປະມານ 90-95% ຂອງກໍລະນີແມ່ນຕົ້ນຕໍ, ຖືກກໍານົດວ່າເປັນຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງເນື່ອງຈາກການດໍາລົງຊີວິດທີ່ບໍ່ສະເພາະແລະປັດໃຈ ທາງພັນທຸກໍາ.[8] ປັດໄຈວິຖີຊີວິດທີ່ເພີ່ມຄວາມສ່ຽງລວມມີ ເກືອ ເກີນໃນອາຫານ, ນ້ໍາຮ່າງກາຍຫຼາຍເກີນໄປ, ການສູບຢາ, ບໍ່ມີການເຄື່ອນໄຫວທາງຮ່າງກາຍ ແລະການໃຊ້ ເຫຼົ້າ.[2][8] 5-10% ຂອງກໍລະນີທີ່ຍັງເຫຼືອແມ່ນໄດ້ຖືກຈັດປະເພດເປັນ hypertension ທີສອງ, ຖືກກໍານົດວ່າເປັນຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງເນື່ອງຈາກສາເຫດທີ່ສາມາດກໍານົດໄດ້ຢ່າງຊັດເຈນ, ເຊັ່ນ: ພະຍາດຫມາກໄຂ່ຫຼັງຊໍາເຮື້ອ, ເສັ້ນເລືອດແດງຂອງຫມາກໄຂ່ຫຼັງແຄບ, ຄວາມຜິດປົກກະຕິຂອງ endocrine, ຫຼືການໃຊ້ ຢາຄຸມກໍາເນີດ.[8]
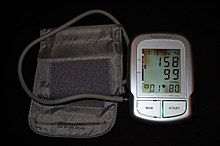
ຄວາມດັນເລືອດຖືກຈັດປະເພດໂດຍສອງການວັດແທກ, systolic (ຕົວເລກທໍາອິດ) ແລະ diastolic (ຕົວເລກທີສອງ).[2] ສໍາລັບຜູ້ໃຫຍ່ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່, ຄວາມດັນເລືອດປົກກະຕິໃນເວລາພັກຜ່ອນແມ່ນຢູ່ໃນລະດັບຂອງ 100-140 ມິນລິເມດ mercury (mmHg) systolic ແລະ 60-90 mmHg diastolic.[9][10] ສໍາລັບຜູ້ໃຫຍ່ສ່ວນໃຫຍ່, ຄວາມດັນເລືອດສູງແມ່ນປະກົດຂຶ້ນຖ້າຄວາມດັນເລືອດທີ່ພັກຜ່ອນຢ່າງຕໍ່ເນື່ອງຢູ່ທີ່ 130/80 ຫຼື 140/90 mmHg.[8][9][10] ຕົວເລກທີ່ແຕກຕ່າງກັນໃຊ້ກັບເດັກນ້ອຍ.[11] ການຕິດຕາມກວດກາຄວາມດັນເລືອດ Ambulatory ໃນໄລຍະ 24 ຊົ່ວໂມງແມ່ນມີຄວາມຖືກຕ້ອງຫຼາຍກ່ວາ ການວັດແທກຄວາມດັນເລືອດ ໃນຫ້ອງການ.[8][1]
ອ້າງອິງ
ດັດແກ້- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "ແມ່ແບບ:Google books". Medical sciences. Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; name "Nai2014" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 "About High Blood Pressure".
{{cite web}}:|archive-url=requires|archive-date=(help);|archive-url=requires|url=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help) Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "CDC2024" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ "Global burden of cardiovascular disease and stroke: hypertension at the core".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789241564373_eng.pdf?ua=1". Global atlas on cardiovascular disease prevention and control.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapter= - ↑ "Treatment options and considerations for hypertensive patients to prevent dementia".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Modifiable Risk Factors and Atrial Fibrillation".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "Hypertension".
{{cite web}}:|archive-url=requires|archive-date=(help);|archive-url=requires|url=(help); Missing or empty|url=(help) - ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 8.5 "Hypertension".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) Cite error: Invalid<ref>tag; name "Lancet2015" defined multiple times with different content - ↑ 9.0 9.1 "2017 ACC/AHA/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/AGS/APhA/ASH/ASPC/NMA/PCNA Guideline for the Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Management of High Blood Pressure in Adults: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ 10.0 10.1 "2023 ESH Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension: Endorsed by the International Society of Hypertension (ISH) and the European Renal Association (ERA)".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ↑ "2014 evidence-based guideline for the management of high blood pressure in adults: report from the panel members appointed to the Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8)".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)